What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines?
Purines and pyrimidines are two main nitrogenous bases common on nucleotides of DNA and RNA. The two compounds are strong building blocks for a variety of organic compounds.
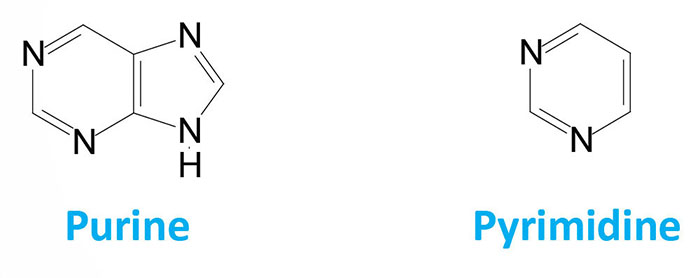
The main difference between pyrimidines and purines is that pyrimidines contain six-membered nitrogenous-containing ring while purines are six-membered nitrogenous-containing ring fused to an imidazole ring.
Read More: Difference between Nitrification and Denitrification
Comparison Table between Purines and Pyrimidines
| Basic Terms | Purines | Pyrimidines |
| Description | It is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound composed of a pyrimidine ring fused with an imidazole ring. | It is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that contains carbon and hydrogen |
| Structure | Double carbon-nitrogen ring with four nitrogen atoms | Single carbon-nitrogen ring with two nitrogen atoms |
| Size | Bigger | Smaller |
| Nucleobases | Adenine, guanine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine | Cytosine, thymine, uracil and orotic acid |
| Catabolism | Produces uric acid | Produces beta-amino acids, ammonia and carbon dioxide |
| Synthesis in Lab | Traube Purine Synthesis | Biginelli Reaction |
| Melting Point | 214 °C | 20-22 °C |
| Molar Mass | 120.11 g mol−1 | 80.088 g mol-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4 | C4H4N2 |
| Biosynthesis | Liver | Various tissue |
| Solubility in Water | 500 g/L | Miscible |
| Function | Enzyme regulation, vitamins, drugs, energy storage, and cell signaling | Production of DNA and RNA, protein and starch synthesis, enzyme regulation and cell signaling |
What Is Purines?
Purines are heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds that contain a six-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms fused to an imidazole ring.
The organic compound occurs in abundance and it is quite common in meat products such as liver and kidney.
Purines are the main building block of DNA and RNA. They are quite vital in building nucleic acids and biomolecules such as ATP, GTP, NAD, cyclic AMP, and coenzyme A.
What Is Pyrimidines?
Pyrimidines are heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds that contain a six-membered ring with two nitrogen atom. It has a structure similar to that of pyridines.
The organic compound comprises of Cytosine, thymine, and uracil as their nucleosides. Also, it has a single hydrogen-carbon ring and two nitrogen atoms.
The end product of pyrimidines is carbon dioxide, ammonia, and beta-amino acids. It has a low melting point when compared to purines.
Main Differences between Purines and Pyrimidines In Point Form
- Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that contains six-membered ring fused to imidazole ring while pyrimidines are an organic compound that contains hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- The nucleobases of purines are adenine and guanine while that of pyrimidines are cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
- The structure of purines contain two hydrogen-carbon rings and four nitrogen atoms while that of pyrimidines contain one hydrogen-carbon ring and two nitrogen atoms
- The melting point of purines is 214 °C while that of pyrimidines is between 20-22 °C.
- The end products of purines are uric acid while that of pyrimidines are carbon dioxide, beta-amino acids, and ammonia
- Purines are synthesized by Traube Purine Synthesis whereas pyrimidines are synthesized by Biginelli Reaction
- Purine have relatively higher boiling point whereas pyrimidines have a comparatively lower boiling point
- The chemical formula of purines is C5H4N4 while that of pyrimidines is C4H4N2.
- The molar mass of purines is 120.11 g mol−1 while that of pyrimidines is 80.088 g mol-1
- The biosynthesis of purines is liver while pyrimidines are common in various tissues.
Frequently Asked Questions (Purines vs Pyrimidines)
- Is Uracil A Purine Or Pyrimidine?
Pyrimidine. Uracil is a nitrogenous base of RNA and it is a pyrimidine. Other nitrogenous bases are cytosine and thymine. Thymine is only common in DNA.
- Are A and G Purines?
Yes. They are two kinds of nitrogenous bases that make up the nucleobases of DNA and RNA.
- Is Caffeine A Purine?
Yes. It is among the naturally occurring purines. Other examples of naturally occurring purines are hypoxanthine, xanthine, theobromine, uric acid, and guanine.
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Haploid and Diploid Cells
- Difference between Genotype and Phenotype
- Difference between DNA and RNA
- Difference between Gene and Allele
- Difference between Allele and Trait
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between purines and pyrimidines is that purines can be created artificially by Traube purine synthesis while pyrimidine can be created artificially by Biginelli Reaction. Purines are quite common in meat products such as liver and kidney.
More Sources and References
- Purine. Wikipedia
- Pyrimidine. Wikipedia