What is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions?
Water movement into and out of the cell is controlled by the cell membranes. Besides that, the solution in which the cell is placed plays a vital role. The solutions can be hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic.
The main difference between hypotonic and hypertonic solution is that hypotonic solution is a solution with lower osmotic pressure while the hypertonic solution is a solution with a higher osmotic pressure.
Comparison Table between Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
| Basic Terms | Hypertonic Solution | Hypotonic Solution |
| Description | It is a solution whose concentration is more than that of the cell sap | It is a solution whose concentration is less than that of the cell sap |
| Solute Concentration | Tend to be quite high | Tend to be quite low |
| Osmotic Pressure | High | Low |
| Solvent Concentration | Low | High |
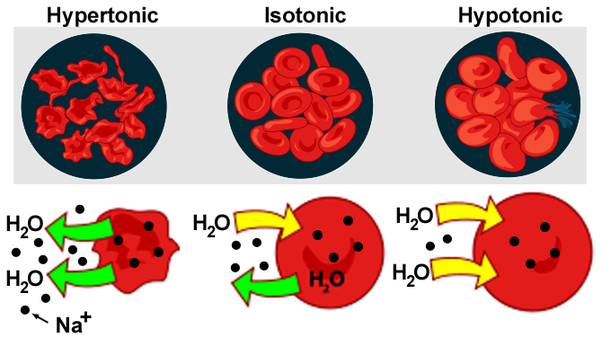
| Effect of the Solution on the Cell | Causes shrinkage | Causes swelling |
| Type of Osmosis | Exosmosis occur | Endosmosis occur |
| Application | Hemorrhage, burn cerebral edema, etc. | Dehydration, hypernatremia, etc. |
| Food Preservation | Quite helpful | Not suitable |
| Solvent Movement | Out of the cell | Into the cell |
| Examples of Intravenous Solutions | D5LR and D5 .45 Na Cl | 0.45 Na Cl and 0.25 Na Cl |
What Is Hypertonic Solution?
Hypertonic solution is a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes in outside than inside the cell.
The cell requires high osmotic pressure to prevent the fluid inside the cell from moving out through the semi-permeable membrane.
The good news is that a hypertonic solution is quite vital for food preservation. Hypertonic solution application is when a fish is deep in salt. It helps kill microbes that cause food decomposition.
What Is Hypotonic Solution?
A hypotonic solution is a solution with a lower solute concentration in the outside than the fluid inside the cell.
The low osmotic pressure help to prevent solute in the cell sap from moving out of the cell through a semi-permeable membrane.
However, excessive intake of water into the cell causes swelling and eventually bursting of the cell. The solution is quite important for the turgidity of the plants.
The presence of cellulose cell walls in plants helps to prevent bursting of cells when placed in hypotonic solutions.
Main Difference between Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions in Point Form
- A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute while the hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solute.
- A hypertonic solution has a higher osmotic pressure while hypotonic solution has a lower osmotic pressure
- A hypertonic solution has a lower solvent concentration while the hypotonic solution has a higher solvent solution
- The hypertonic solution causes the cell to shrink while the hypotonic solution causes the cell to swell
- Exosmosis is the type of osmosis present in hypertonic solution while endosmosis happen in a hypotonic solution
- Hypertonic solution is helpful in food preservation while the hypotonic solution is not suitable for food preservation
- The main application of the hypotonic solution is dehydration and hypernatremia while that of the hypertonic solution is hemorrhage, burn, and cerebral edema
Frequently Asked Questions (Hypertonic Solution Vs Hypotonic Solution)
- Is Normal Saline Hypertonic?
Yes. It has a lot of solute concentration of sodium chloride.
- Is An Egg In Vinegar Hypotonic Or Hypertonic?
Hypertonic. It draws water from the surrounding and then increases in size.
- Is Distilled Water Hypertonic?
Hypotonic solution. It has less amount of solute and more solvent.
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Turgor Pressure and Wall Pressure
- Difference between Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis
- Difference between Endosmosis and Exosmosis
- Difference between Turgidity and Flaccidity
- Difference between Isotonic and Isometric
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between hypotonic and hypertonic solutions is that hypotonic solution is a dilute or less concentrated solution whereas hypertonic is a more concentrated solution.
These two concepts are quite vital when it comes to the description of tonicity and osmosis. Also, it describes the key function of the semi-permeable membrane.
More Sources and References
- Tonicity. Khan Academy
- Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions. NCBI