What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
Nucleic acid is made up of DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are quite common in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Both tend to be polymers of nucleotides and they play an essential role in genetics.
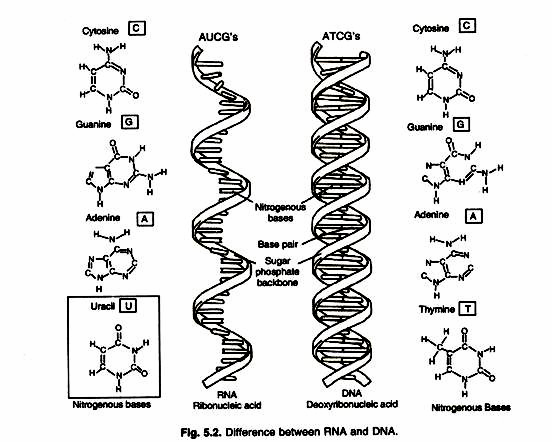
The core difference between DNA and RNA is that RNA contains ribose sugars while DNA contains de-oxy-ribose. Besides that, RNA uses Uracil instead of thymine which is present in DNA. Let’s find out more:
DNA Meaning
DNA is an abbreviation of deoxyribonucleic acid and it tends to carry genetic information that is quite vital in living organisms.
DNA stranded are normally double-stranded. It tends to replicate and store genetic information. It is considered to be the blueprint for all genetic information in organisms.
The main nitrogenous base of DNA is thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine(C), and adenine (A). They are crucial in determining the genetic code.
RNA Meaning
RNA is an abbreviation of ribonucleic acid. It is a nucleic acid that is directly involved in the synthesis of proteins.
The core function is to act as a messenger by conveying messenger from DNA to help in the control of protein synthesis.
RNA tends to contain sugar ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U).
Comparison Chart: DNA vs RNA
| Basic Terms | DNA | RNA |
| Stands For | Deoxyribonucleic Acid | Ribonucleic Acid |
| Sugar Portion | 2-Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Helix Geometry | B-Form (A or Z also present). | A-Form. |
| Predominant Structure | Double strand | Single strand |
| Length of Nucleotide Chain | Long-chain | Short Chain |
| Nitrogenous Base | Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. | Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil. |
| Propagation | Self-replication | Synthesized from DNA |
| Proportionality of Purine and Pyrimidine | Equal | Not proportional |
| Ultraviolet Damage | Highly affected by UV | Relatively resistant to UV damage |
| Hydrogen Bond | Between complementary bases of nitrogen such as (A-T, C-G). | Occurs in the coiled parts. |
| location | Nucleus and mitochondria | Nucleus, cytoplasm, and ribosomes |
| Leaving | Does not leave the nucleus | Leave nucleus as mRNA |
| Stability | Fairly stable due to C-H bond | Unstable in alkaline condition |
| Renaturation after melting | Slow | Fast |
| Types | Occur in two types like intranuclear and extranuclear. | Occur in three types like m-RNA, t-RNA, and rRNA. |
| Fixed or Variable | Quantity is fixed | Quantity is variable |
| Lifespan | Long | Short |
| Core Function | Long term storage and transmission of genetic information | Transfer genetic code from the nucleus to ribosomes for protein synthesis. |
| Base Pairs | Adenine and Thymine pair (A-T) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) | Adenine and Uracil pair (A-U) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) |
| Catalytic Activity | Do not have catalytic activity | Ribozymes are the main catalytic activity |
| The effect in alkaline solution | Stable | Unstable |
| Grooves | Comparatively smaller grooves | Comparatively larger grooves |
| Histone Proteins | Associated with it | Not associated at all |
| Pyronin Dye effect | Stain green | Stain red |
| Azureph Thalate Dye effect | Stain Blue | Stain red |
Core Differences between DNA and RNA
- DNA is an abbreviation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid while RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid.
- The sugar portion of DNA is 2-Deoxyribose while that of RNA is Ribose.
- The helix geometry of RNA is A-form while that of DNA is B-form
- DNA is a double-stranded molecule while RNA is a single-stranded molecule
- The propagation of DNA is self-replication while that of RNA is synthesized from DNA.
- DNA is highly damaged by UV while RNA is relatively resistant to UV damage
- DNA is present in mitochondria and nucleus while RNA is present in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and ribosomes.
- DNA does not leave the nucleus while RNA tends to leave in the form of mRNA.
Core Similarities between DNA and RNA
- Both act as genetic materials
- Both are polymers of nucleotides
- Both have pentose sugars
- Both contain hydrogen bond
Comparison Video
Conclusion
Understanding the core difference between DNA and RNA with a comparison chart has made things easier. You can also use the point forms for deeper understanding and finer details. Good luck with your research and preparation for exams.
You May Also Like
- Acute Vs Chronic Disease
- Active Transport Vs Passive Transport
- Primary Succession Vs Secondary Succession
- Inhalation Vs Exhalation
- Cellulose Vs Starch Vs Glycogen