What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles?
The human body is made up of muscles. These muscles contain soft tissues such as actin and myosin. These tissues are responsible for the contraction and expansion of muscle cells.
Research shows that the body organ system has over 700 muscles. Examples of organ systems are the digestive system and internal organs. These muscles are divided into voluntary and involuntary.
The main difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles is that the former is controlled by the central nervous system whereas the latter is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
You May Also Like: Difference Between Tendons and Ligaments
Comparison Table (Voluntary vs Involuntary Muscles)
| Basic Terms | Voluntary Muscles | Involuntary Muscles |
| Meaning | These are muscles moved by the free will of a person. These muscles are associated with the skeleton system. | These are muscles that are not controlled by the will or consciousness of a person. These muscles are associated with organs that exhibit slow contraction and relaxation. |
| Alternative Names | Striated muscles or skeletal muscles. | Nonstriated muscles or smooth muscles. |
| Location | Attached to the bones by tendons. | The lining of the walls of the internal organs like the intestines or stomach. |
| The shape of the Cell | Thick, long, cylindrical, and unbranched with a nucleus located towards the periphery. | Thin, long, and spindle-shaped with a nucleus located at the center. |
| Type of Cell | Multinucleated with a large number of mitochondria. | Uninucleated with fewer mitochondria. |
| Sarcolemma | Thicker | Thinner |
| Sarcomeres | Present in muscle fibers | Absent in muscle fibers |
| Intercalated Discs | Absent | Present in cardiac muscle |
| Control | Controlled by will or conscious | Cannot be controlled by the will |
| Nervous System | Controlled by the somatic nervous system | Controlled by the autonomic nervous system |
| Nerve Stimuli | It is created from outside of the nervous system | Generated from within the muscle since they are myogenic. |
| Type of Contraction and Relaxation | Rapid and robust | Rhythmic and slower |
| Energy Requirement | More energy for contraction and relaxation of muscles | Less energy for contraction and relaxation of muscles |
| Fatigue and Rest | Tend to experience fatigue faster and require regular intervals of rest | Do not experience fatigue. Hence no need for resting. |
| Significance | Enhance the movement of body parts and locomotion of the body. | Aid the passage of fluids and food in the digestive system. |
| Examples | Biceps
Triceps Quadriceps Hamstring Pectoral muscles Abdominal muscles Diaphragm |
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle lining of: Intestinal tract Blood vessels Urogenital tract Respiratory tract |
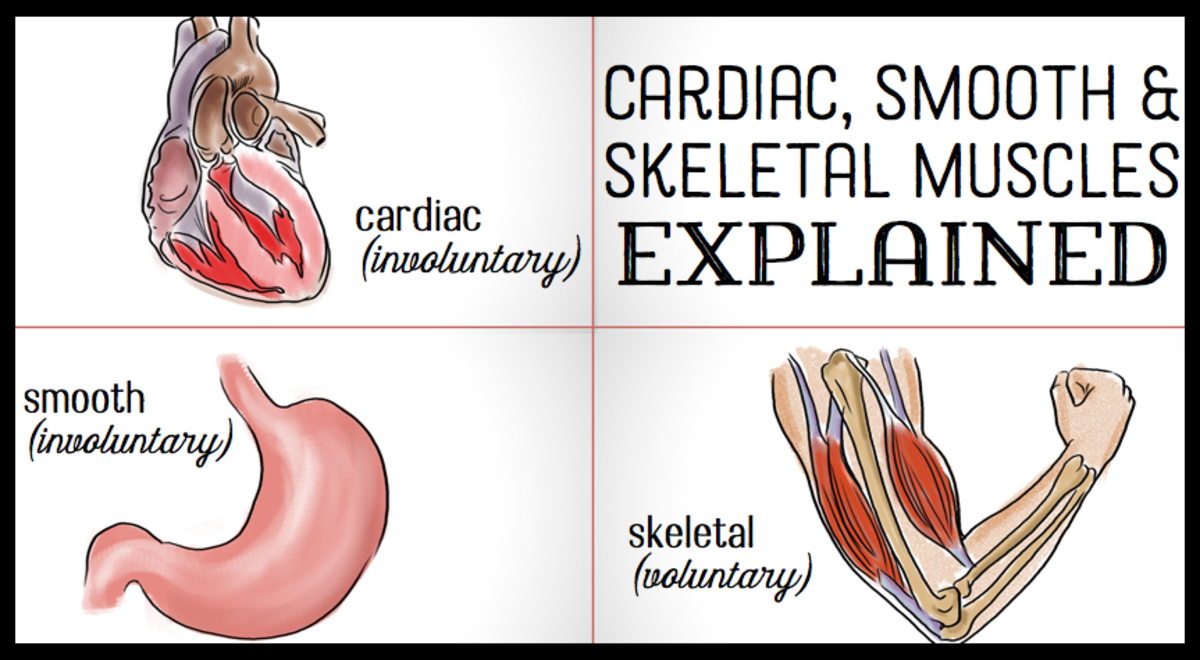
What Are Voluntary Muscles?
Voluntary muscles are those muscles that move by the free will of a person. These muscles are associated with the skeleton system.
These muscles are responsible for the movement of all vertebrates and they attached to the bones by tendons. Voluntary muscles are long and present near bones.
Each muscle cell is nucleated and the nucleus is located at the periphery of the cell. The muscles are surrounded by sarcolemma which is a special cell membrane.
The cell membrane is thick and it is responsible for connecting muscle fibers to each other and the connective tissues. These muscle fibers contain sarcomeres for relaxation and contraction.
Examples of voluntary muscles are the biceps, the triceps, the quadriceps, the diaphragm, pectoral muscles, abdominals, hamstrings, etc.
You May Also Like: Difference between Vertebrates and Invertebrates
What Are Involuntary Muscles?
These muscles are also known as smooth muscles or non-striated muscles. They are mostly found in the lining of internal organs like the stomach, intestinal tract, blood vessels, and urinary tract.
The smooth muscles have cells that are long, thin, and spindle-shaped with the centrally located nucleus. The sarcolemma surrounding the muscle cells are thin and connect muscle fibers with each other.
Cardiac muscle is an example of involuntary muscle. It usually differs from others in terms of structures and function.
The contraction and relaxation of involuntary muscles move slowly and occur at intervals of time. It is the reason why the muscles do not experience fatigue that needs a rest.
Examples of involuntary muscles are cardiac muscle and smooth muscles that occur in the lining of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, blood vessels, and intestinal tract.
You May Also Like: Difference between Arteries and Veins
Main Difference between Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles
- Voluntary muscles are multinucleated whereas involuntary muscles are uni-nucleated.
- Voluntary muscles are attached to the bones while involuntary muscles occur in the lining of internal organs.
- Voluntary muscles have high energy requirements and involuntary muscles have low energy requirements.
- Voluntary muscle cells have a nucleus on the periphery whereas involuntary muscle cells have a nucleus at the center.
- Voluntary muscles have thick sarcolemma whereas involuntary muscles have thin sarcolemma.
- Voluntary muscles are controlled by the somatic nervous system whereas involuntary muscles are controlled by thin sarcolemma.
- Voluntary muscles experience rapid and robust contraction whereas involuntary muscles experience slow and rhythmic contraction.
- Voluntary muscles experience fatigue whereas involuntary muscles do experience fatigue.
- Voluntary muscles enhance the movement of body parts and locomotion of the body while involuntary muscles aid the internal movement of the organs.
- Examples of voluntary muscles are the diaphragm, pharynx, abdominal wall tongue, and muscles of the middle ear while those of involuntary muscles are blood vessels, Alimentary tracts, ducts of glands, and Urogenital tracts.
You May Also Like: Difference between Large Intestines and Small Intestines
In Conclusion
The human body consists of 40% muscle which also contributes to body weight. These muscles consist of actin and myosin. These components define the shape and length of the muscle.
Voluntary and involuntary muscles are the type of major muscles in the body. The main difference between involuntary and voluntary muscle is based on structure and function.
Take the time to read through the guide and get to know the hidden facts between involuntary and voluntary muscles.
Keep in mind that voluntary muscles are associated with skeleton muscles and involuntary muscles with smooth and cardiac muscles.
More Sources and References
- https://www.medicinenet.com/involuntary/definition.htm
- https://www.britannica.com/video/143176/muscles-motor-cortex-brain-hypothalamus-regions