What is the difference between single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA?
Genetics is the study of inheritance. The genetic makeup of an organism is transmitted via DNA replication. The DNA can either be single-stranded or double-stranded.
The core difference between single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA is that single-stranded DNA has a star shape while double-stranded DNA has a linear form.
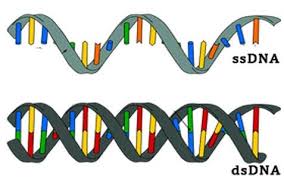
What Is Single-Stranded DNA?
Single-stranded DNA is a star-shaped genetic makeup and it is less stable. It behaves as randomly coiled polymers and it tends to be present in some viruses.
What Is Double-Stranded DNA?
Double-stranded DNA is a linear form of genetic makeup and it is quite stable. It behaves like a rigid rod-like structure and it is present in all organisms.
Comparison Chart: Single-Stranded DNA vs. Double-Stranded DNA
| Basic Terms | Single-Stranded DNA | Double-Stranded DNA |
| Appearance | Have a stellate or star shape | Have a linear or filamentous shape |
| Composition Relationship | No relationship | Thymine is equal to adenine. Guanine is equal to cytosine |
| The ratio of A: T | 0.77 | 1 |
| The ratio of G:C | 1.3 | 1 |
| Stability | less stable | More stable |
| Resistance to formaldehyde | Prone to action | Quite resistant |
| UV absorption | Increases from 20 to 900c | Increases from 0 to 800c |
| Morphology | Randomly coiled polymer | Rigid rod-like structure |
| Occurrence | Few viruses | All organism |
| Chargaff rule | Do not follow | Tend to follow |
| The ratio of purine and pyrimidine | Tend to vary | 1 |
Core Difference between Single-Stranded DNA and Double-Stranded DNA
- Single-stranded DNA occur in few viruses while double-stranded DNA occurs in all organism
- Double-stranded DNA follow chargaff rule while single-stranded DNA do not follow chargaff rule
- The ratio of purine and pyrimidine in single-stranded DNA tend to vary greatly while in double-stranded is one
- Thymine is equal to adenine in double-stranded DNA while there is no such relationship in single-stranded DNA
- Double-stranded DNA has linear or filamentous form while single-stranded has stellate or star shape form
- Single-stranded DNA have randomly coiled polymer while double-stranded DNA has a rigid rod-like structure
- The UV absorption of single-stranded DNA increases from 20 to 900c while that of double-stranded increases from 0 to 800c
- Double-stranded DNA is more stable while single-stranded DNA is less stable
- Double-stranded DNA is resistant to the action of formaldehyde while single-stranded is highly prone to the action of formaldehyde
- The ratio of guanine to cytosine in double-stranded DNA is one while in single-stranded DNA is 1.3
- The ratio of thymine to adenine in double-stranded DNA is one while in single-stranded is 0.77
Similarities between Single-Stranded DNA and Double-Stranded DNA
- Both deal with genetic material
- Both are polymers of nucleic acid
- Both contain purine and pyrimidine
- Both contain a nitrogenous base
- Both absorb UV light
You May Also Like:
- Difference between DNA and RNA
- Difference between Deoxyribose and Ribose
- Difference between Linkage and Crossing Over
- Difference between Continuous and Discontinuous Variation
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA is that single-stranded DNA has a stellate or star shape and double-stranded has rigid rod-like structures. Both deal with the genetic makeup of an organism.