what is the difference between resonance and mesomeric effect?
The behavior of electrons during the formation of molecular bonds tend to differ in elements except in carbon atoms. The organic reaction is normally influenced by the electromeric effect, resonance effect, mesomeric effect, and inductive effect among others.
The lesson provides a detailed insight into the difference between resonance and mesomeric effect with a comparison chart. We have also discussed the similarities between resonance and mesomeric effects.
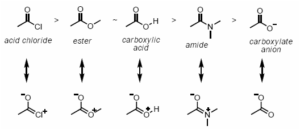
What Is Resonance Effect?
The resonance effect is typically used to describe the lone pair and the bond electron pair of a molecule that determines the chemical structure of the molecule.
The resonance effect is responsible for the polarity of the molecule and the effect is observed in the double bond.
The number of lone electrons and pi-electron bond determines the several forms of resonance in a molecule.
The resonance effect can either be positive or negative. Positive resonance effect describes the delocalization of electrons having a positive charge which occurs in the stabilization of positive charge while negative resonance describes the delocalization of electrons in a molecule having a negative charge which occurs in the stabilization of negative charge.
What Is Mesomeric Effect?
The mesomeric effect describes the stabilization of a molecule by the use of different functional groups or substituents. Where some of these functional groups are electron donors while other electron-withdrawing groups.
The phenomenon occurs due to the difference between the negativity values of atoms in these functional groups. For instance, higher negativity indicates higher electron-donating ability.
The negative mesomeric effect describes the effect of electron-donating or release of these substituents. The positive mesomeric effect describes the effect of electron-withdrawing of these substituents.
Comparison Chart: Resonance Vs Mesomeric Effect
| Basic Terms | Resonance Effect | Mesomeric Effect |
| Meaning | It describes the concept of interaction between the lone electron pair and bond electron pair of a molecule that determines the chemical structure | It is a concept that describes stabilization of a molecule by use of a functional group |
| Causative Agent | Lone electron pair adjacent to the double bond | Presence of a functional group or conjugated system |
| Different Types | Positive and negative resonance effect | Positive and negative mesomeric effect |
| Polarity | Causes polarity of a molecule | Has no effect as far as polarity is concern |
Core Difference between Resonance and Mesomeric Effect
- Resonance effect is a concept that describes the lone pair electron and bond pair electron of a molecule determining the chemical structure whereas the mesomeric effect describes the stabilization of a molecule by use of a functional group
- Resonance effect is caused by a lone electron pair adjacent to double bond whereas the mesomeric effect occurs due to the functional group
- Resonance effect has two types such as positive and negative resonance effect while the mesomeric effect has two types like negative and positive resonance effect
- Resonance effect determine the polarity of a molecule unlike the mesomeric effect
Read More: Difference between Disodium EDTA and Tetrasodium EDTA
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between resonance and the mesomeric effect is that the resonance effect outline how the lone electron pair and bond electron pair of a molecule determine the chemical structure of the molecule whereas the mesomeric effect describes the stabilization of a molecule by use of a functional group.