What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA?
DNA is a genetic material quite common in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Besides that, the chemical composition and structural features of DNA are the same.
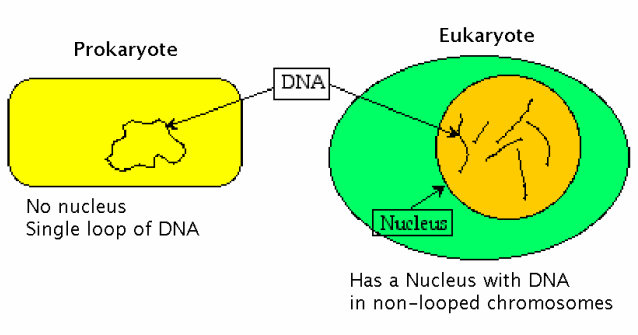
The core difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA is that prokaryotic DNA occurs as a covalently closed circular form while eukaryotic DNA occurs in a linear form.
Prokaryotic DNA Definition
Prokaryotic DNA occurs freely in the central position of the cytoplasm. They occur in a covalent close circular form.
What You Need to Know about Prokaryotic DNA
- The DNA content tend to be small
- DNA occurs freely in the cytoplasm
- DNA consists of a single molecule
- Has small DNA segments
- DNA has fewer genes
- Have more of GC than AT content
Eukaryotic DNA Definition
Eukaryotic DNA is found within the nucleus. It occurs as a linear form of DNA with two ends. Eukaryotic DNA has high content.
What You Need to Know about Eukaryotic DNA
- DNA occurs inside the nucleus
- DNA contains mitochondria and plastids
- Have several molecules of DNA
- Nuclear DNA is linear
- The AT content is higher than GC
- Has numerous number of genes
Comparison Chart: Prokaryotic DNA Vs Eukaryotic DNA
| Basic Terms | Prokaryotic DNA | Eukaryotic DNA |
| Found | Cytoplasm | Nucleus |
| DNA content amount | Less | More |
| Structure | Circular and double-stranded | Linear and double-stranded |
| Histone Proteins | Do not interact with histone | Tend to interact with histone |
| Introns | Absent | Present |
| Number of Chromosomes | Organized into a single chromosomes | Organized in numerous chromosomes |
| Transposons | Absent | Present |
| Number of Genes | Small number | More number |
| DNA Replication | Occur in the cytoplasm | Occur in the nucleus |
| Chromosome | No chromosomes are formed | Chromosomes are formed in the nucleus |
| Quantity of the DNA | Less | More |
| Nucleosome | Absent | Present |
| Codes | 300 to 500 proteins | Over 4000 proteins |
| Organelles | Absent | Present |
Core Difference between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic DNA
- Eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus while that of prokaryotic DNA in the cytoplasm
- The DNA content in Eukaryotic DNA is more while that of prokaryotic DNA is less
- Prokaryotic DNA occur in circular form while eukaryotic occur in linear form
- Eukaryotic DNA interact with histone while prokaryotic DNA do not
- Eukaryotic DNA has introns while prokaryotic DNA do not have
- Prokaryotic DNA has single organized chromosomes while eukaryotic DNA has numerous chromosomes
- Eukaryotic DNA has more genes while prokaryotic DNA has fewer genes
- Eukaryotic DNA experience nucleosome formation unlike prokaryotic DNA
- Chromosomes are formed in the nucleus of eukaryotic DNA but absent the nucleus of prokaryotic DNA
- DNA replication of prokaryotic DNA occurs in the cytoplasm while in eukaryotic DNA occur in the nucleus
- Eukaryotic DNA consists of transposons which is absent in prokaryotic DNA
- Prokaryotic DNA has about 300 to 500 protein synthesis while eukaryotic DNA has over 4000 protein synthesis
Similarities between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA
- Both DNA is double-stranded
- Both DNA contain purine and pyrimidine
- Both follow chargaff rule
- Both DNA strands are antiparallel to each other
- Both experience DNA replication
- Both exhibit extrachromosomal genetic material
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Translation
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Comparison Video
Summary
DNA is a hereditary material in an organism. These organisms can either be prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The core difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA is that eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus while that of prokaryotic DNA is located in the cytoplasm.