What is the difference between plasmolysis and deplasmolysis?
Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the two subdivisions of osmosis. Endosmosis involves the gaining of water and exosmosis which involve the loss of water by the cell. They normally involve the movement of water into and out of the cell.
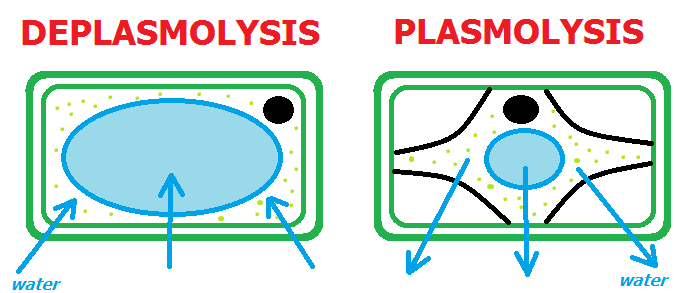
The core difference between plasmolysis and deplasmolysis is that plasmolysis is the constriction of the protoplast as a result of exosmosis while deplasmolysis is the swelling of protoplast as result of endosmosis.
What Is Plasmolysis?
Plasmolysis is the constriction of the protoplast as a result of water loss during exosmosis. It makes the protoplast to shrink and get separated from the cell wall.
The hypertonic solution is responsible for the occurrence of the process since it has a higher concentration of the solute than the cell sap.
Plasmolysis can either be convex or concave plasmolysis. Convex plasmolysis makes the cytoplasm to round up into a convex shape. Concave plasmolysis makes the cytoplasm to produce concave pockets.
What Is Deplasmolysis?
Deplasmolysis is the swelling of the protoplast as a result of water gain during endosmosis. The process results in the swelling of plasmolyze cells.
It occurs when the cell is placed in a hypotonic solution since the water potential of the outside is higher than that of the cell sap.
An isotonic solution has similar concentration like that of the cell sap hence neither plasmolysis or deplasmolysis takes place.
Comparison Chart: Plasmolysis Vs Deplasmolysis
| Basic Terms | Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis |
| Meaning | This refers to the shrinking and separation of protoplasm from the cell wall. | This refers to the swelling of protoplasm towards the cell wall. |
| Movement of Water | Move out of the cell | Move into the cell |
| Type of Osmosis | Exosmosis | Endosmosis |
| Type of Solutions | Hypertonic | Hypotonic |
| Solute Concentration | The surrounding solute concentration is higher than the cytosol | The surrounding solute concentration is lower than the cytosol |
| Water Potential | The surrounding water potential is less than the cytosol | The surrounding water potential is higher than the cytosol |
| Result | Cell shrinkage | Cell turgidity and swelling |
| Osmotic Pressure | Very low | Very high |
Core Differences between Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis
- Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the cell due to dehydration while deplasmolysis is the swelling of the cell
- Plasmolysis make the cell to lose water while deplasmolysis make the cell to gain water
- Osmotic pressure in plasmolysis is very low while in deplasmolysis is very high
- Plasmolysis results in cell shrinkage while deplasmolysis result in cell turgidity and swelling
- The surrounding water potential is less than the cytoplasm in plasmolysis while in deplasmolysis the surrounding water potential is higher than that of cytoplasm
- The solute concentration of the surrounding is higher than that of cytoplasm in plasmolysis while lower than that of cytoplasm in deplasmolysis
- Type of solution that causes plasmolysis is hypertonic and hypotonic causes deplasmolysis
- Type of osmosis experience by plasmolysis is exosmosis while endosmosis cause deplasmolysis
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Osmosis and Diffusion
- Difference between Endosmosis and Exosmosis
- Difference between Turgor Pressure and Wall Pressure
Comparison Video
https://youtu.be/AQ-EG6WPOw8
Summary
Plasmolysis causes the water to move out of the cell causing shrinking due to dehydration. Deplasmolysis causes water to move into the cell resulting in swelling of the cell.