What is the difference between reciprocal and non-reciprocal translocation?
Chromosomal translocation is a situation that results in the unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. It can either be balanced or unbalanced translocation.
The main types of chromosomal translocation are reciprocal and Robertsonian translocation. The lesson provides a distinction between reciprocal and non-reciprocal translocation.
The main difference between reciprocal and non-reciprocal translocation is that reciprocal translocation is a chromosomal abnormality caused by the exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes while non-reciprocal translocation is responsible for the movement of a chromosomal segment from one non-homologous chromosome to another.
Read More: Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription
Comparison Table (Reciprocal Translocation vs Non-Reciprocal Translocation)
| Basic Terms | Reciprocal | Non-Reciprocal |
| Meaning | It is a translocation responsible for an exchange of chromosomal segments with two non-homologous chromosomes | It is a translocation responsible for the movement of a chromosomal segment from one non-homologous chromosome to another. |
| Number of Chromosomal Segment | Two chromosomal segments | One chromosomal segment |
| Type of Rearrangement | Two chromosomal segments exchange between two loci of non-homologous chromosomes | One chromosomal segment move to another locus of non-homologous chromosomes |
| Effect | Causes infertility, miscarriage and children abnormalities | Result in cell proliferation, neuroblastoma, and especially lung cancers |
| Transferring of Chromosome Segment | Two-way transfer | One way transfer |
What Is Reciprocal Translocation?
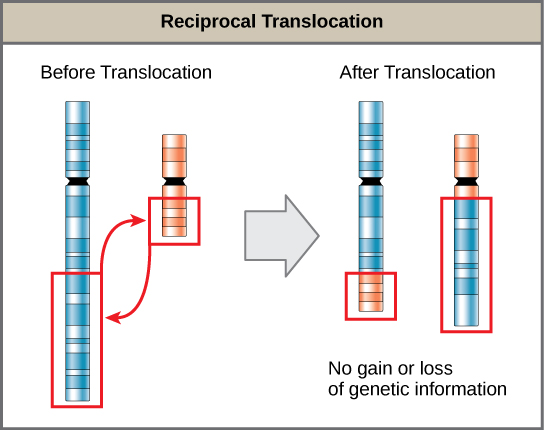
It is a type of chromosomal translocation responsible for the exchange of two chromosomal segments between non-homologous chromosomes.
Balance reciprocal translocation does not result in the loss of genetic materials. Hence, it does not cause diseases but results in infertility and miscarriages.
Genetic counseling and genetic testing help to identify families that carry reciprocal translocation. Reciprocal translocation can occur both in somatic cells and gamete cells during error in mitosis and meiosis respectively.
What Is Non-Reciprocal Translocation?
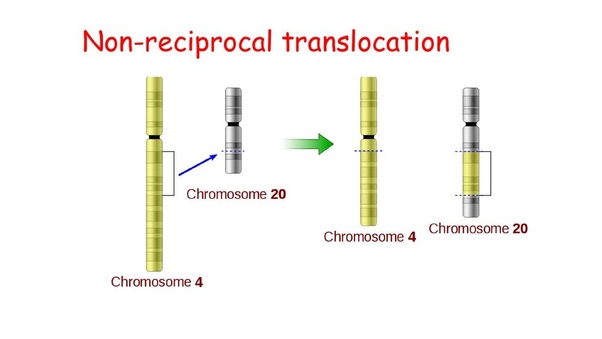
It is a type of chromosomal translocation that results in the movement of the chromosomal segment from one non-homologous chromosome to another.
The translocation results in the transfer of genes from one locus of a genome to another. It also causes telomere instability.
In addition, telomere dysfunction results in the impaired regenerative capacity of hepatocytes and an increased cirrhosis formation.
Some of the common effects of the translocation are neuroblastoma and several cancer types. It occurs due to increased cell proliferation.
Main Difference between Reciprocal and Non-Reciprocal Translocation
- Reciprocal translocation is the exchange of chromosome segment between non-homologous chromosomes whereas non-reciprocal translocation is the movement of chromosome segment to a different non-homologous chromosome
- Reciprocal translocation results in no loss or gain in genetic material whereas non-reciprocal translocation is where one chromosome lose while the other gain
- Reciprocal translocation is a two-way transfer while non-reciprocal is a one-way transfer
- Reciprocal translocation is where two-segment exchange with each other whereas non-reciprocal translocation is where another segment does not exchange with another broken first segment
- Reciprocal translocation causes children abnormalities, infertility and miscarriages whereas non-translocation result in several cancer types and neuroblastoma
Similarities between Reciprocal and Non-Reciprocal Translocation
- Both are a type of chromosomal translocation
- Both bring massive rearrangement of chromosomal structure
- Both involve the movement of chromosome segment from one locus to another
- Both bring structural changes to chromosomes
- Both cause loss or gain of chromosome function
- Both causes abnormalities and several cancer types
Read More: Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Reciprocal vs Non-Reciprocal Translocation FAQs
Is Reciprocal Translocation Balanced?
Yes. There is no loss of genetic material and the individual is phenotypically normal. However, it causes a change in chromosomal structures.
What Causes Reciprocal Translocation?
It is caused by Robertsonian translocation. The phenomenon occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes get attached.
Can I Get Pregnant With A Balanced Translocation?
Yes. But the condition is normally associated with more difficulty conceiving and are at a greater risk of recurrent miscarriage than those without it.
What Happens With A Chromosomal Inversion?
It occurs when a single chromosome undergoes breakage and rearrangement within itself.
Comparison Video
Summary
Chromosomal translocation is a change in the position of the chromosome segment to another region of the same chromosome or to another chromosome.
The movement of chromosomes tends to occur in the form of reciprocal and non-reciprocal translocation. The identification can be done in the form of genetic counseling and genetic testing.
More Sources and References
Translocations. NCBI
Human Chromosome Translocations and Cancer. Nature Education