What is the difference between linkage and crossing over?
Mendel’s law of independent assortment tends to describe the inheritance of patterns of chromosomes except linkage and crossing over. The crossing over and linkage tends to involve the study of genes on chromosomes.
The core difference between linkage and crossing over is that linkage is the tendency of the genes on chromosomes to remain together and pass them to next-generation while crossing over is the exchange of genes to break linkages and result in new linkages.
What Is Linkage?
Linkage is the tendency of DNA sequence to remain intact on the chromosome and pass the genes to the next generation. The tendency is known as genetic linkage and genes linking together on a chromosome are linkage groups.
Completely linked genes are those located in close proximity on the same chromosome while partially or incompletely linked genes are those that are located far apart on the chromosome.
What Is Crossing Over?
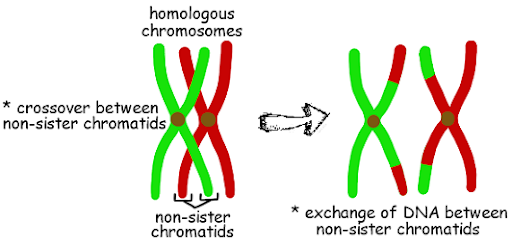
Crossing over is the exchange of genes with the aim of breaking the old genes and result in new gene formation. It occurs on non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Crossing over is a natural genetic recombination process that occurs commonly during the pachytene stage of prophase 1 of meiosis.
Comparison Chart: Linkage vs Crossing Over
| Basic Terms | Linkage | Crossing Over |
| Definition | It is the tendency of genes that are closed together on the chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis stage | It is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes resulting in new chromatids with the different genetic makeup |
| Significance | Ensures all the genes on the chromosomes are inherited together | Ensures separation of genes on the same chromosomes into segregation of different chromosomes |
| Distance Between Two Genes | Genes have close proximity on the chromosomes | Genes are far apart on the chromosomes |
| Maintenance of the Parental Traits | Parental traits are maintained | Result in changes in parental traits |
| Influence of the Age | Decreases with age | Increases with age |
| Variations | Decreases chances of variation in new offspring | Increases chances of variation in offspring |
Core Differences: Crossing Over vs Linkage
- Linkage ensure the genes are kept together for inheritance while crossing over ensure there is the separation of genes to segregate into different gametes
- Linkage genes have close proximity together on the chromosomes while crossing over genes are far apart on the chromosomes
- Linkage is the tendency of DNA sequence to remain together in a chromosome and pass to the next generation while crossing over is the exchange of genes to result in a different offspring with different genes
- Linkage produce parental type while crossing over the result in recombination
- Linkage increases with age increase while crossing over decreases with age increase
- Crossing over the result in new varieties while linkage results in maintenance of a newly improved variety
Similarities between Linkage and Crossing Over
- Both are a type of gene interaction on the same chromosomes
- Both are the exceptions of Mendel’s law of segregation.
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Deoxyribose and Ribose
- Difference between Continuous and Discontinuous Variation
- Difference between Single-Stranded DNA and Double-Stranded DNA
Comparison Video
Summary
The main difference between crossing over and linkage is that crossing over the result in the exchange of genes to form new offspring with different genetic makeup while linkage is the tendency of the DNA sequence that is close together on the chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis of sexual reproduction