What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle quite common in animal and plant cells. It is grouped into the smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The article provides a detailed insight into the core difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum in tabular form for easier understanding.
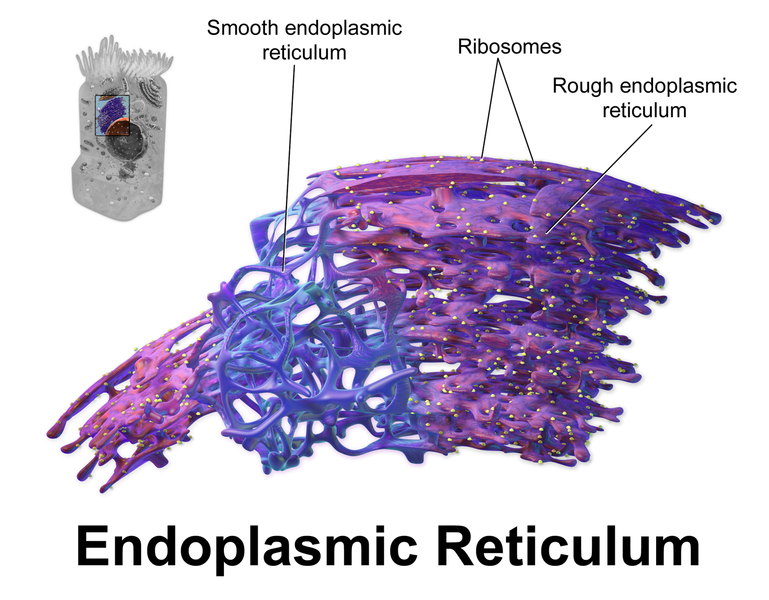
What Is Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle responsible for secretion, production, and storage of lipids. It also helps to facilitate the metabolism of carbohydrates and the manufacture of new membranes.
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is also known as Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum and it is abbreviated as SER. It is formed from the Rough ER after the loss of ribosomes.
SER plays a crucial role in mammalian cells of detoxification reactions from the drugs and other metabolic wastes.
SER does not take part in the synthesis of proteins but the core function of the organelle is responsible for transporting synthesized proteins.
What Is Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle responsible for the synthesis of proteins and its transportation.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is also known as Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum and it is abbreviated as RER. It has 80S ribosomes which bring uneven surface.
Comparison Chart: Smooth Vs Rough
| Basic Terms | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| Core Difference | Has smooth appearance due to the absence of ribosomes on the outermost surface | It has a granular appearance due to the presence of ribosomes on the outer surface. |
| Location | Near the plasma membrane | Near the nucleus |
| Core Function | Formation of lysosomes | Formation of Golgi body |
| Structure | Do not have pores | Has pores at the point of ribosomes attachment for passage of synthesizing materials. |
| Enzymes | Have enzyme for detoxification | Do not have enzymes |
| Presence | Quite more in cells with lipids for steroid metabolism | Quite plenty in cells with proteins |
| Ribophorins | Absent | Present for attachment of ribosomes |
| Origin | Rough endoplasmic reticulum after the loss of ribosomes | Nuclear envelope |
| Ribosomes | Absent | Present |
| Composed of | Tubules. | Cisternae. |
Core Difference Between Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- SER does not bear ribosomes on their surface while RER normally contains ribosomes on their membrane.
- SER formed from of vesicles and tubules whereas RER formed from cisternae and a few tubules.
- SER helps in the synthesis of glycogen, lipids, and steroids while RER help in the synthesis of proteins and enzymes.
- RER is responsible for the synthesis of lysosomes from the Golgi apparatus while SER is responsible for sphareosomes.
- RER tend to have Ribophorins while SER does not.
- SER contains enzymes for detoxification while RER enzymes are absent
- SER originated from rough endoplasmic reticulum while RER originated from the nuclear envelope.
- RER has Ribophorins for attachment of ribosomes while SER does not have it.
- RER has tiny pores below the ribosomes’ attachment point for passage of synthesized materials while SER does not have pores.
You May Also Like:
- Difference Between Cell and Tissue
- Difference between Anabolism and Catabolism
- Difference between Nucleoside and Nucleotide
- Difference between Chromatid and Chromosome
- Difference between Heterochromatin and Euchromatin
Comparison Video
Summary
Both SER and RER play a vital role in the synthesis and storage of macromolecules. SER produces lipids and stores them while RER produce proteins and store them as well.
The core difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum is that RER has ribosomes on its membrane while SER does not have ribosomes.
More Sources and References
- Endoplasmic Reticulum. Britannica
- Endoplasmic Reticulum. Wikipedia