What is the difference between sapwood and heartwood?
Every tree tends to experience both sapwood and heartwood. These two kinds of wood play a significant role in the growth of a tree. However, many people tend to find it hard to make a comparison between them.
The biological discussing highlight some of the core difference between sapwood and hardwood with a comparison table. We have also gone ahead and highlight the similarities between sapwood and heartwood in the discussion.
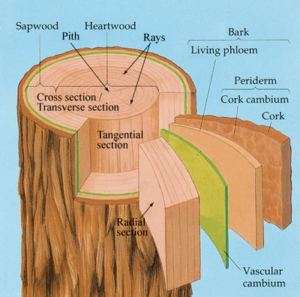
What Is a Sapwood?
Sapwood is also known as laburnum. This is the outermost layer of the wood and the living wood in a growing tree. The core function of the sapwood is to bring water from the roots to the leaves. When the water becomes scarce, the sapwood helps to distribute the stored water from the roots to the rest part of the tree.
The wood tends to be lighter in color and it is highly susceptible to pathogens which make it less durable. The living cells in the wood are responsible for the structural support of the tree wall. It also forms a base where nutrients are stored to be used in case of scarcity.
What Is a Heartwood?
Heartwood is also known as duramen. This is the wood that occurs at the center of an old stem and it is the dead part of an old tree. The cells around the region are dead but they tend to remain intact to serve another purpose.
Some of the popular chemical compounds responsible for the darker color of the heartwood are resins, terpenes, and phenols. These chemical compounds also make the wood resistant to pathogens and insects hence making it quite durable.
Comparison Chart: Sapwood Vs Heartwood
| Basic Terms | Sapwood | Heartwood |
| Meaning | Refers to the outermost layer of the wood | Refers to the dense central region of the wood |
| Alternative names | Laburnum | Duramen |
| Location | Occur at the peripheral region | Occur at the center region |
| Cells | Has living cells | Has dead cells |
| Color | Lighter in color | Darker in color |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavyweight |
| Hard or Soft | Soft | Hard |
| Xylem | Xylem vessel and tracheid not plugged | Xylem vessel and tracheid are plugged with tyloses |
| Composition | More cellulose | More lignin |
| Conductivity | Serve as conductor | Serve as insulator |
| Function | Transport of water and nutrients | Offer structural support |
| Durability | Less durable due to attack by pathogens | Quite durable due to resistant attack from pathogens |
Core Differences between Sapwood and Heartwood
- Sapwood is the outermost region of the wood in old trees whereas heartwood is the central region of the wood in the oldest trees
- Sapwood is also known as laburnum while heartwood is also known as duramen.
- Sapwood is light in color while the heartwood is darker in color
- Sapwood comprise of living cells while heartwood comprise dead cells
- The vessels of the heartwood are plugged with tyloses whereas those of sapwood is not plug
- The main function of heartwood is to offer mechanical support whereas sapwood enhance the transport of water and nutrients
- Sapwood is less durable while heartwood is quite durable
- Sapwood consists of more cellulose while heartwood consists of lignin
- Sapwood serve as a conductor while heartwood serve as an insulator
- Sapwood is quite soft while the heartwood is quite hard
- Sapwood is lightweight and heartwood is heavyweight
- Heartwood is suitable for making furniture while sapwood is not suitable at all.
Similarities between Sapwood and Heartwood
- Both comprise of secondary xylem
- Both are derived from cambium vascular
- Both offer mechanical support
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between sapwood and heartwood is that sapwood occurs in the periphery region of the wood while heartwood occurs in the inner region of the wood from old stems. Besides that, they are both derived from vascular cambium and they offer mechanical support.