What is the difference between protoxylem and metaxylem?
Xylem is a complex tissue comprising of different cells. Xylem tissue is responsible for conducting water and minerals from the roots to the other parts of the plant.
Xylem consists of xylem tracheid, vessels, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma. The secondary function of the xylem is to offer mechanical support to the plant.
The core difference between protoxylem and metaxylem is that protoxylem is the first formed part of the xylem while metaxylem is the second part of the xylem.
What Is Protoxylem?
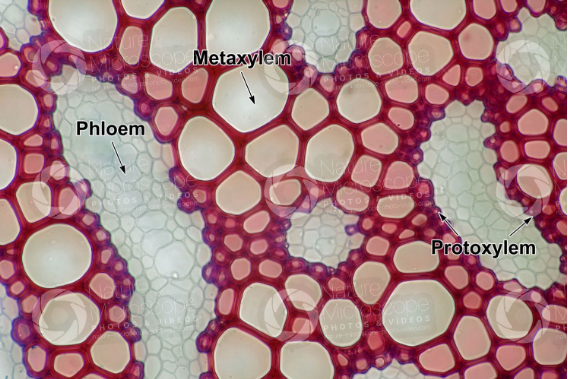
Protoxylem is the primary part of the xylem that develops first during primary growth. The part tends to mature faster than the other parts of the plant.
Young stems have protoxylem on the outside and tend to have smaller cells. The protoxylem has narrow lumen since it contains narrow vessel elements and tracheid.
The protoxylem cells do not experience lignification but show annular and spiral thickening. It also contains a large amount of parenchyma.
What Is Metaxylem?
Metaxylem is part of the primary xylem that develops after protoxylem. The part tends to mature after the completion of major plant organs.
It occurs inside the plant stem and it is marked with the wider lumen. Besides that, it has wider tracheid and vessel elements.
The metaxylem show lignification and the vessel show scalariform, reticulate, and pitted thickenings in their secondary cell walls.
The tissue is quite efficient in the conduction of water and minerals. It has more of xylem fibers and less of parenchyma cells.
Comparison Chart: Protoxylem Vs Metaxylem
| Basic Terms | Protoxylem | Metaxylem |
| Meaning | Refer to the first-formed xylem part during primary growth | Refer to the second formed part of the xylem after protoxylem |
| Formation | Formed first | Formed after completion of protoxylem |
| Differentiation | Procambium | Fascicular cambium |
| Significance in Maturation | Mature before other plant organs | Mature after completion of other plant organs |
| In the Stems of Seed Plants | Occur close to the center | Occur on the periphery of the stem |
| In the Root of Vascular Plant | Occur on the periphery of the root | Occur on the closet of the center |
| Tracheids and Parenchyma | Has a large amount of parenchyma and less of tracheid | Has a large amount of tracheid and fewer parenchyma cells |
| Size of Tracheids | Tracheid and vessel elements have a narrow lumen | Tracheid and vessel elements have a wider lumen |
| Secondary Wall Thickening of Tracheids | Either annular or spiral | Either reticulate or pitted |
| Tyloses | Absent | Present |
| Water Conduction efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient |
| Xylem Fibers | Absent | Present |
| Subjection to the Stress and Strain | Highly susceptible | Less susceptible |
| Formation of Lysigenous Cavity | Involve in the formation of a lysigenous cavity | Does not get involved in the formation of a lysigenous cavity |
| Flexibility | Tend to stretch | Not able to stretch |
Core Differences between Protoxylem and Metaxylem In Point Form
- Protoxylem is the first formed part of the vascular bundle while metaxylem is the part of xylem formed after protoxylem
- Protoxylem mature before other plant organs while metaxylem mature after completion of other plant organs
- Protoxylem is arranged towards the center in the stems while metaxylem is arranged on the periphery of the stem
- Protoxylem is arranged towards the periphery in the roots while metaxylem is arranged around the center of the root
- Protoxylem contain less amount of treachery elements while metaxylem contain more of treachery elements
- Protoxylem contain more of parenchyma cells while metaxylem contain less amount of parenchyma cells
- The tracheary elements in protoxylem have narrow lumen while in metaxylem have a wider lumen
- The cell thickening of protoxylem either show annular or spiral thickening while metaxylem show either reticulate or pitted thickening
- Protoxylem is prone to stress and strain while metaxylem is not prone to strain or stress
- Protoxylem are fused together in monocot to form cavity while metaxylem does not form any cavity
- Metaxylem have tracheid fibers while protoxylem do not have fibers
- Metaxylem have tylose while protoxylem do not have tylose
- Protoxylem is less efficient in water and mineral transport while metaxylem is quite efficient in water conduction
- Protoxylem have comparatively smaller cells while metaxylem have comparatively larger cells
- Lignification is less extensive in protoxylem while more extensive in metaxylem
Similarities between Protoxylem and Metaxylem
- Both are responsible for water and mineral conduction
- Both contain living and dead cells
- Both develop primary meristem
- Both contain tracheid, vessels, and parenchyma
- Both develop in primary vascular bundles
You May Also Like:
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between metaxylem and protoxylem is the morphological orientation. Metaxylem has wider lumen while protoxylem has a narrower lumen. But both are responsible for mineral and water conduction.