What is the difference between natural and synthetic polymers?
Polymers are made out of small units known as monomers. These macromolecules are classified according to structures, chemical, and physical properties. Natural and synthetic polymers are the basic classification of polymers.
The discussion provides insight into the core difference between natural and synthetic polymers with examples.
What Are Natural Polymers?
Natural Polymers are polymers that can be found naturally in the environment. The majority of chemical compounds in the bio-system are polymer compounds.
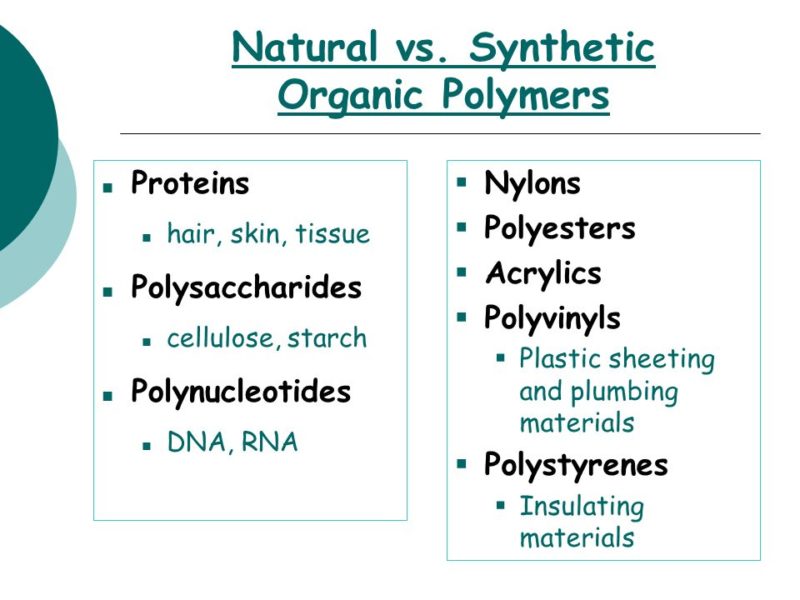
Natural polymers are grouped into polysaccharides, polyamides, and polynucleotides. Polysaccharides are made out of several units of monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, galactose, etc. Polysaccharides are present in plants as carbohydrates and in animals as glycogen
Polyamides are proteins and other natural polymers with peptide bonds. The presence of a number of amide groups all over the polymer results in polyamides. Amino acids are monomers proteins. Polynucleotides include DNA and RNA.
Polypeptides are small proteins due to the peptide bonds. Examples of proteins are silk, wool in plants while enzymes such as amylase in animals.
What Are Synthetic Polymers?
Synthetic polymers are artificially produced polymers by human beings. The process of production is normally done in factories and laboratories.
The type of chemical reaction used in their production help in the classification of synthetic polymers. Most polymers are synthesized by condensation and addition.
Synthetic polymers can either be organic or inorganic polymers. Examples of synthetic polymers are polyethylene, polypropylene, Teflon, polystyrene, etc.
Comparison Chart: Natural Vs Synthetic Polymers
| Basic Terms | Natural Polymers | Synthetic Polymers |
| Meaning | These are polymers that occur naturally in the environment | These are polymers artificially made by human beings |
| Occurrence | Naturally | Artificially |
| Production | Biological process | Chemical Reaction |
| Degradation | Easily degraded by biological process | Hard to degrade by biological process |
| Types | Polyamides, polysaccharides, and polynucleotides. | Inorganic polymers and organic polymers. |
| Rubber | Tree latex | Polymerization of several monomers |
| Examples | DNA, cellulose, silk, wool, and proteins. | Polyethylene, polyester, nylon, Teflon, and epoxy. |
Core Difference Between Natural and Synthetic Polymers
- Natural polymers are polymers that occur naturally in the environment whereas synthetic polymers are polymers that are artificially made by humans
- The nature of the occurrence of natural polymers is naturally while that of synthetic polymers is artificial.
- Natural polymers are produced from biological processes while synthetic polymers are produced through chemical processes
- Most natural polymers are easily degraded by biological processes while synthetic polymers are hard to degrade by biological processes
- Types of natural polymers are Polyamides, polysaccharides, and polynucleotides while those of synthetic polymers are organic and inorganic polymers
- Examples of natural polymers are DNA, cellulose, silk, wool, and proteins while those of synthetic polymers are polyethylene, polyester, nylon, Teflon, and epoxy.
Read More: Difference between Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between natural and synthetic polymers is that natural polymers occur naturally in our environment while synthetic polymers are artificially made by human beings.