What is the difference between mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism?
Interaction in a community entails mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. These modes of nutrition tend to confuse many students doing biological science courses.
The lesson provides detailed insights into the difference between mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism with a comparison chart.
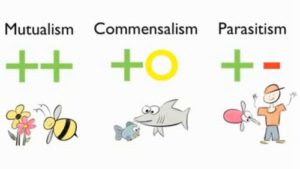
What is Mutualism?
Mutualism refers to a symbiotic relationship where both organisms tend to benefit. The main aim of this symbiotic relationship is to bring balance in the life cycle.
The common types of mutualism are nutrition, defense, transport, and shelter. Examples of situations where mutualism is exhibited are bees and flowers, digestive bacteria and the human body, coral reef, and algae.
What is Commensalism?
Commensalism refers to a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits more while the other tends to be affected. An example is hermit crabs use the shells of dead snails for homes.
The phenomenon happens to enhance one organism to get food from the other species. The main aim of the relationship is for locomotion, shelter, food, and defense.
What is Parasitism?
Parasitism is a relationship where one species which is the parasite benefits while the other species which is the host gets harmed.
Many species of animals can either be host or parasite during their various stages of life. Examples are roundworms which are parasites in many mammals like human beings.
Comparison Chart: Mutualism vs Commensalism vs Parasitism
| Mutualism | Commensalism | Parasitism |
| It is a symbiotic relationship where both species benefits | It is a symbiotic relationship where one species benefits more than the other. | It is a relationship where the parasite benefits while the host gets harmed |
| The relationship is obligatory | The relationship is non-obligatory | The relationship can either be obligatory or facultative |
| Result in a positive interaction | Result in a positive interaction | Result in a negative interaction |
| All species are dependent on each other for survival | One species tend to benefit while the other gets affected | One species benefits while the other get harm |
| An example of the relationship is a Sea Anemone and a Clownfish. | An example of the relationship is climbers taking the support of trees to grow. | Example of the relationship is Salps and Phronima. |
Differences between Mutualism, Commensalism and Parasitism
- Mutualism result in a positive interaction, commensalism result in positive interaction and parasitism result in a negative interaction
- Mutualism is where all species benefits, commensalism is where one species benefits more than the other and parasitism is where one species benefits more while the other gets affected
- The relationship of mutualism is obligatory, commensalism is obligatory while that of parasitism is either obligatory or facultative
- Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both species benefits, commensalism is where one species benefits more than the other whereas parasitism is where one species benefits while the other gets harm
- An example of mutualism is sea anemone and a clownfish, of commensalism, is when climbers taking the support of trees to grow and parasitism is an infestation of roundworms in the stomach of mammals.
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism is that mutualism is where all the species benefits, commensalism is where one species benefit more than others and parasitism is where one species benefits while the other get harm.