What is the difference between metals, non-metals and metalloids?
The periodic table tends to indicate all elements that have been discovered on earth. These elements are classified based on their chemical and physical properties.
The main difference between metals, non-metals and metalloids are that metals are elements that are hard, malleable, fusible, shiny, ductile and good conductors.
Non-metals do not have properties present in metals whereas metalloids are elements that have intermediate properties of both metals and non-metals.
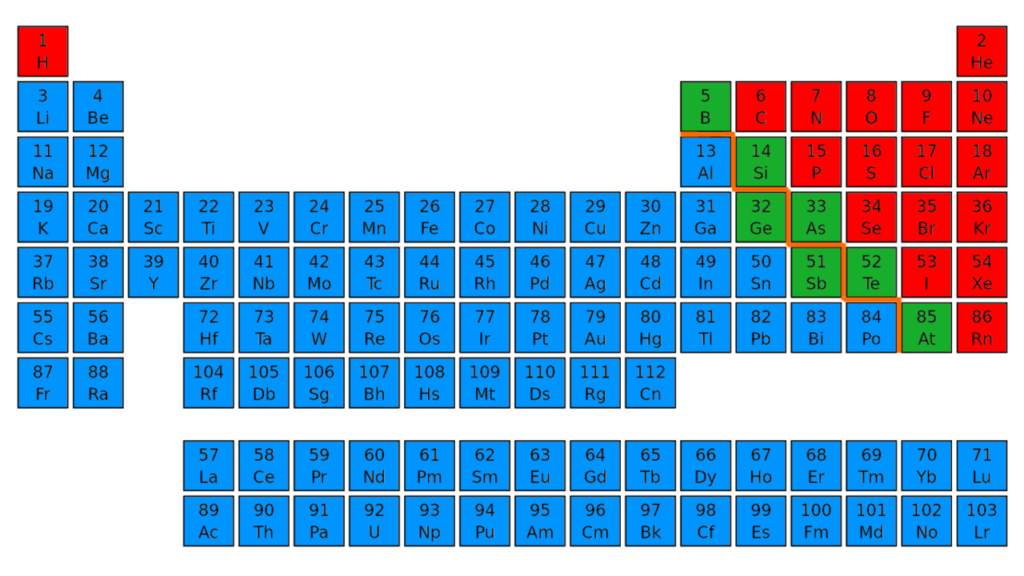
Comparison Table (Metals vs Non-Metals vs Metalloids)
| Metals | Non-Metals | Metalloids |
| These are elements that exhibit the highest degree of metallic behaviour | These are elements that do not exhibit metallic behaviour | These are elements that possess some properties of both metals and non-metals |
| Found on the left side of the periodic table | Found on the right side of the periodic table | Found in the middle of the periodic table |
| Located in s, p, d, and f blocks. | Located in s and p blocks. | Located in p blocks |
| Shiny appearance | Dull appearance | Both shiny and dull in appearance |
| High level of both thermal and electrical conductivity | Low conductivity of thermal and electrical | Good level of thermal and electrical conductivity |
| Low electronegativity | High electronegativity | Neither possess the high or low value of electronegativity |
| Malleable and ductile | Do not show malleability and ductility | Do not show malleability and ductility |
| Examples are Lithium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Barium, Lead, Indium, Bismuth, Iron, Copper, Zinc, Nickel, etc | Examples are Iodine, Bromine, Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Sulfur, Phosphorous, etc. | Examples are Arsenic, Tellurium, Antimony, Polonium, Tennessine, etc. |
Read More: Difference between Acid and Base
What are the Metals?
These are elements found on the left side of the periodic table and they tend to exhibit metallic behaviour.
Metals are classified as basic metals, alkali metals, transition metals, alkaline earth metals, lanthanides and actinides.
Examples of metals are Lithium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Barium, Lead, Indium, Bismuth, Iron, Copper, Zinc, and Nickel, etc.
Basic Metals
These are elements that exhibit metallic behaviour. Examples are Bismuth, Aluminium, Gallium, Indium, Thallium, Lead, and Nihonium.
Transition Metals
These are elements that show colour complexities and they have a subshell of d or f partially filled. Examples are Scandium, Vanadium, Titanium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Copper, Nickel, Rhodium, Palladium, Lanthanum, Tungsten, Silver, Gold, Mercury, and Platinum.
Alkali Metals
These are elements found on the far left of the periodic table of IA group. Examples of the metals are Lithium, Potassium, Sodium, Rubidium, Cesium, and Francium. These metals are very reactive.
Alkaline Earth Metals
These are elements in the IIA group of the periodic table. They are shiny and less reactive than alkali metals. Examples are Magnesium, Beryllium, Radium, Barium, Calcium, and Strontium.
What Are the Properties of Metals?
- High lustre
- Metallic Appearance
- Solid at room temperature except for mercury
- Good conductor of electricity and heat
- High malleable and ductile
- Have a high melting point
- Tend to lose electrons
- Oxidize in air and saltwater
What are Non-Metals?
These are elements found on the right side of the periodic table. These elements have low melting and boiling points.
Examples are Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, Selenium, and Hydrogen (exception).
What Are the Properties of Non-Metals?
- Have dull appearance
- Typically brittle
- The bad conductor of heat and electricity
- Less dense
- Low melting and boiling point
- Gain electrons in a chemical reaction
What Are Metalloids?
These are elements that exhibit characteristics of both metals and non-metals. They are commonly used in electronic device and computer as semiconductors.
Examples are Boron, Germanium, Silicon, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, Polonium, and Tennessine. These elements can be used to make polymers, ceramics and batteries.
What Are the Properties of Metalloids?
- They are either shiny or dull
- Conduct heat and electricity
- Good semiconductors
- Exist in several forms
- Show malleability and ductility
- Either gain or lose an electron in the chemical reaction
Main Difference between Metals, Non-Metals and Metalloids
- Metals exhibit a high degree of metallic behaviour while non-metals do not possess metallic behaviour and metalloid exhibit both metallic and non-metallic behaviour
- Metals are found on the left side of the periodic table whereas non-metals are found on the right side of the periodic table and metalloids are found on the middle of the periodic table
- Metals are located in s, p, d, and f blocks, non-metals are located in s and p blocks whereas metalloids are located in p blocks of the periodic table
- Metals have high thermal and electrical conductivity while non-metals tend to be low and metalloids are good conductors
- Metals have low electronegativity, non-metals have high electronegativity and metalloids have either low or high value of electronegativity
- Metals tend to exhibit malleability and ductility whereas nonmetals and metalloids do not display the properties
- Metals have a shiny appearance, nonmetals have dull appearance and metalloids can either be shiny or dull in appearance
- Examples of metals are Lithium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Barium, Lead, and Indium. Examples of non-metals are Iodine, Bromine, Helium, Neon, and Argon while that of metalloids are Arsenic, Tellurium, Antimony, Polonium, Tennessine, etc
Similarities between Metals, Non-Metals and Metalloids
- Both loss or gain electrons in chemical reactions
- Both are found on the periodic table
- Both elements occur in nature
- Both are either shiny or dull in appearance
- Both elements are quite important
Read More: Difference between Purines and Pyrimidines
Metals vs Non-Metals vs Metalloids FAQs
What Do Metalloids Metals and Nonmetals Have In Common?
Metalloids tend to exhibit some properties of metals and non-metals. Metalloids can conduct electricity but not as well as metals.
Is BR a Metal or Non-Metal?
It is a non-metal since it belongs to group 17 of the periodic table. The element has similar properties to those of fluorine, chlorine, and iodine.
Is A Metalloid A Metal?
A metalloid is an element that exhibits properties of a metal and non-metal. It can either be classified as a metal or non-metal.
Comparison Video
Summary
Understanding the properties of metals, non-metals and metalloids will help tell the difference. The properties of metalloids are the intermediaries of between metals and non-metals.
We have highlighted the difference between metals, nonmetals and metalloids in tabular form for easier understanding.
More Sources and References
- The Periodic Table. Angelo Education
- Properties of Elements. Wikipedia