What is the difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity?
Active immunity is the immunity induced into the body of an organism through exposure to a foreign antigen. It is grouped as humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
The core difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity is that humoral immunity is mediated through antibodies while cell-mediated immunity is enhanced by activating TH cells and cytotoxic T as well as lymphocytes CTLs.
Take the time to read through the lesson and get detailed facts about the differences in the comparison chart as well as point forms.
What Is Humoral Immunity Response?
Humoral immune is a response immunity that is mediated through antibodies. It is the core defense mechanism against extracellular microbes. It responds to pathogens quickly.
It triggers the B cells to produce antibodies that bind with foreign antigen then neutralized them through phagocytosis.
What Is Cell-Mediated Immunity?
Cell-mediated immunity is the immune response that identifies and destroys infected cells to prevent the spread of viruses or bacteria.
The immune response trigger development of T cells which are released into the thymus and circulate between the peripheral lymphoid tissue and the blood.
The process helps to identify foreign antigens and get rid of them immediately. The immune response it quite stronger than humoral immune.
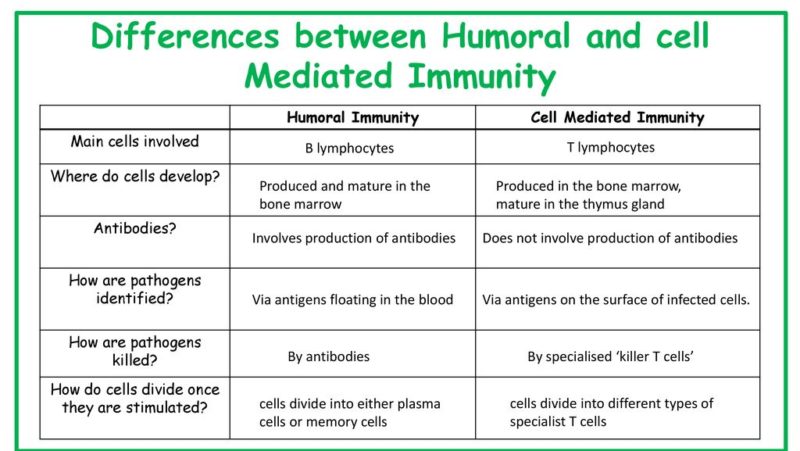
Comparison Chart: Humoral Vs Cell-Mediated
| Basic Terms | Humoral Immunity | Cell-mediated Immunity |
| Onset | Rapid | Delay |
| Activation | Differentiation of plasma B cells and secretion of antibodies | Secretion of cytokines |
| Main cells | B-cells which are generated and mature in the bone marrow | T-cells generated in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus |
| Pathogens | Protect against extracellular pathogens | Protect against intracellular pathogens |
| Meaning | Antibodies are formed | Antibodies are not formed |
| Antigen Detection | Antibodies | Receptors |
| Examples of cells | Only TH cells | CD4+ and CD8+ cells |
| Cancer cells | Cannot be eliminated | Can easily be eliminated |
| Rejection | Involve in early graft rejection | Participate in organ transplant rejection |
| Core function | It protects against extracellular bacterial and viral pathogens. | It protects against intracellular bacterial and viral pathogens. |
Core Difference between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity
- The humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies while cell-mediated immunity by T cells.
- Humoral immune response results in the production of antibodies but cell-mediated immunity does not.
- Receptors are used in cell-mediated immunity to detect antigens while in humoral immunity antibodies are used to detect antigens.
- T cells receptors in cell-mediated immunity bind antigens while antibodies in humoral immunity bind antigens.
- Cell-mediated immunity protects against intracellular pathogens while humoral immunity against extracellular pathogens
- Cell-mediated immunity eliminates tumor cells and offers protection against cancer while humoral immunity cannot.
- Cell-mediated immunity facilitates delayed hypersensitivity while humoral immunity mediates immediate hypersensitivity.
Core Similarities between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity
- Both are types of active immunity
- Both are effective against wide varieties of pathogens
- Have lag period
- Immunological memory is present in both
- Both ineffective in immune-deficient individuals
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Arteries and Veins
- Difference between Enzymes and Hormones
- Difference between Macronutrients and Micronutrients
Comparison Video
Summary
Understanding the core difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity is quite important as far as active immunity is concern. Use the comment section to share some of your views and suggestions.
More Sources and References