According to the NIH, about 60% of Americans have COPD. Most of these people are unaware of the disease in their bodies. Earlier detection of the symptoms and diagnosis is important in preserving lung function.
Another research shows that people suffering from COPD usually have asthma. The condition is responsible for causing COPD. Going for dual diagnosis of asthma and COPD is crucial to avoid lethal effects.
So, what is the difference between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? The former result in the dryness of cough while the latter result in coughs that yields mucus. Besides that, asthma symptoms usually disappear between episodes and COPD symptoms progressively worsen.
Both these respiratory diseases are marked by obstruction of the airway. Asthma is diagnosed during childhood while COPD is diagnosed in adults. Many medics usually mistakenly treat asthma instead of COPD.
Comparison Table (Asthma vs Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
| Basic Terms | Asthma | COPD |
| Age | Diagnosed in children. | Symptoms show up in adults over 40 years. |
| Main Symptoms |
|
|
| Nature of Cough | Dry cough | Cough yields mucus |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam and medical history of allergies in children. | CT scans to measure breath in adults and spirometry. |
| Classical Presentation | Young patients experience recurrent episodes of symptoms. | Older patients especially smokers or former smokers experience progressive symptoms that are worsening. |
| Causes |
|
|
| Risky factors |
|
|
| Medical Treatment |
|
|
| Lifestyle Changes |
|
|
| Airway inflammation | Eosinophilic | Neutrophilic |
What Is Asthma?
It is a respiratory disease characterized by spasms of the bronchioles due to inflammation and narrowing of airways in the lungs.
Asthma usually results in difficulty breathing due to allergic reactions. There are many substances that trigger this respiratory condition.
The common symptoms of asthma are shortness of breath, chest tightness, and wheezing. The respiratory condition is can be reversed through medical treatment.
Asthma condition might get worse when an individual is exposed to cold air, exercise and allergens. Most symptoms of asthma usually disappear between episodes.
What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
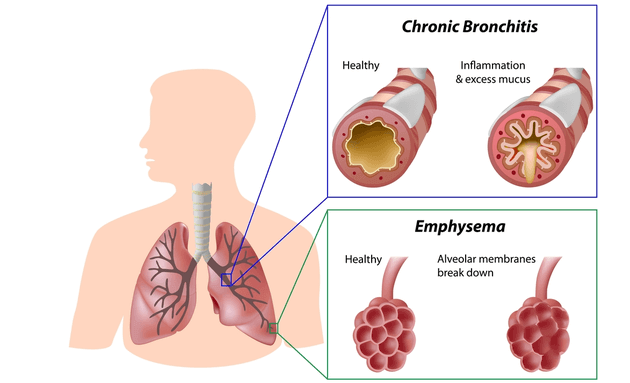
It is yet another respiratory condition characterized by chronic interference with the lung airflow that impairs breathing. The respiratory disease is not fully reversible as seen in asthma.
Examples of COPD symptoms are shortness of breath, recurrent coughing that yields mucus, clearing throat, and progressive exercise tolerance.
The main cause of COPD is smoking. It is further divided into chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The recurrent symptoms are progressively worsening with time.
Other people susceptible to COPD are former smokers, passive smokers, and those suffering from asthma. Exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes might also cause COPD.
There is no cure for COPD. But patients are given treatment in form of oxygen therapy, medicine, lung transplant and advised to cease smoking.
Main Differences between Asthma and COPD
- Asthma is diagnosed in childhood while COPD in adults over 40 years.
- Asthma results in dryness in cough whereas COPD causes a productive cough.
- Asthma is caused by genetic make-up, environmental factors, and allergens whereas COPD is caused by continuous smoking.
- Asthma results in periodic airflow obstruction and eosinophilic airway inflammation. COPD results in progressively worsening airflow obstruction and neutrophilic airway inflammation.
- Airflow restriction in a patient with asthma is reversible while for those with COPD is irreversible.
Similarities between Asthma and COPD
- Both are respiratory diseases.
- Both result in obstruction of airways.
- Both need physical exams for diagnosis.
- Both require air filtration for prevention.
- Both are preventable through different methods.
In Conclusion
Both COPD and asthma are long-term respiratory conditions. These conditions cannot be cured. Asthma can easily be controlled whereas COPD usually worsens over time.
Sticking to prescribed medical plans will help to reduce the severity of asthma and COPD symptoms. These medications also help to prevent complications.
More Sources and References
- https://www.medicinenet.com/copd_vs_asthma_differences_and_similarities/article.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/asthma.html
- https://medlineplus.gov/copd.html