What is the difference between aromatic and aliphatic compounds?
Almost all organic compounds are made up of carbon and hydrogen. These compounds are further grouped as aromatic and aliphatic compounds.
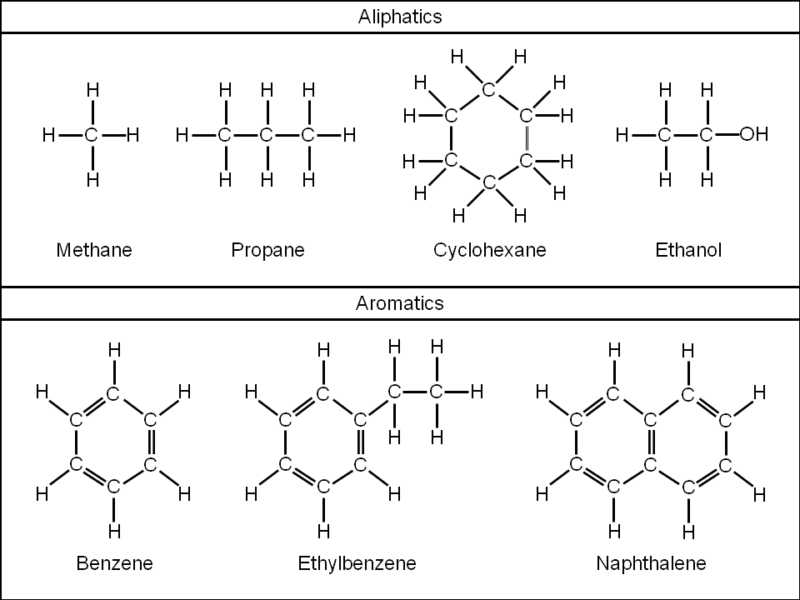
The core difference between aromatic and aliphatic compounds is that aromatic compounds contain benzene ring while aliphatic compounds do not contain a benzene ring.
What Are Aromatic Compounds?
Aromatic compounds are organic compounds that have distinct benzene rings. The aromatic ring has a double bond between the hydrocarbons.
The benzene ring has six carbon atoms that are cyclically bonded with the alternating double bond.
The conjugation process experienced in aromatic compound tends to give them a different chemical behavior when compared to other compounds.
Examples of aromatic compounds are benzene, toluene, naphthalene xylene, and aniline
What Are Aliphatic Compounds?
Aliphatic compounds are hydrocarbons that do not have benzene rings. The organic compound is also known as a non-aromatic compound.
The aliphatic compounds are further grouped as cyclic hydrocarbon, linear, branched, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The carbon atoms in the compound can be attached to hydrogen atoms either as single or double or triple bonds.
The saturated hydrocarbon is formed when the carbon and hydrogen atoms are single-bonded. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is formed when carbon and hydrogen atoms are either double or triple bonded.
Examples of aliphatic compounds are alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and derivatives.
Comparison Chart: Aromatic Vs Aliphatic Compounds
| Basic Terms | Aromatic Compounds | Aliphatic Compounds |
| Meaning | They are hydrocarbons that contain a benzene ring | They are organic compounds that do not contain a benzene ring |
| Reactions | React under special conditions | React more freely and easily |
| Types | Only cyclic | Either cyclic or linear |
| Saturation Potential | Occur as saturated only | Occur as either saturated or unsaturated |
| Conjugation | Tend to be conjugated due to the alternating double bond | Not conjugated |
| Benzene Ring | Present | Absent |
| Odor | Tend to have a sweet pleasant smell | Tend to be odorless |
| Electron delocalization | Can observe as an electron delocalized cloud | No electron delocalization |
| Flame test | A sooty flame is produced when burnt | A sooty flame is not produced when burnt |
| Examples | Benzene, toluene, naphthalene xylene, and aniline | Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes |
Core Difference between Aliphatic and Aromatic Compounds
- Aromatic compounds are organic compounds with benzene ring in their structure while aliphatic compounds are hydrocarbon without benzene ring in their structure
- Aromatic compounds react under special conditions while aliphatic compounds react freely and easily
- Cyclic is the only type of aromatic compound while linear and cyclic are the two types of aliphatic compounds
- Aromatic compounds are saturated always whereas aliphatic compounds are either saturated or unsaturated
- Aromatic compounds tend to conjugate due to alternating double bond while aliphatic compound do not conjugate
- The aromatic compound has a benzene ring while aliphatic compound do not
- Aromatic compounds produce sweet smell while aliphatic compounds are odorless
- Aromatic compounds produce a sooty flame when burnt while aliphatic compounds do not produce a sooty flame when burning
- Examples of aromatic compounds are benzene, toluene, naphthalene xylene, and aniline while aliphatic compounds examples are alkenes, alkanes, and alkynes
- Aromatic compounds observe electron delocalization while aliphatic compounds do not.
Read More: Difference between Compound and Mixtures
Comparison Video
Summary
Aromatic compounds contain benzene rings hence react under special conditions. Aliphatic compounds do not contain benzene ring but react more easily and can either be saturated or unsaturated.