What is the difference between Giemsa stain and wright stain?
Staining is the process of being able to differentiate between cells of an organism by making them more visible. The process is quite common in viewing specimens on a microscope.
The main difference between Giemsa stain and wright stain is that Giemsa stain is used to stain chromosomes to help in understanding chromosome aberrations while wright stain is used to differentiate blood cell type.
Read More: Difference between Bioburden and Microbial Limit Test
Comparison Table between Giemsa Stain and Wright Stain
| Basic Terms | Giemsa Stain | Wright Stain |
| Description | It is a stain which plays a huge role in cytogenetics and histopathological diagnosis of malaria | It is a hematologic stain which helps to differentiate blood cell types |
| Scientist | Gustav Giemsa | James Homer Wrist |
| Content | A mixture of Azure B, methylene blue, and eosin dye | A mixture of eosin and methylene blue dyes |
| Smears | Entail use of both thick and thin smears | Uses only thin smears |
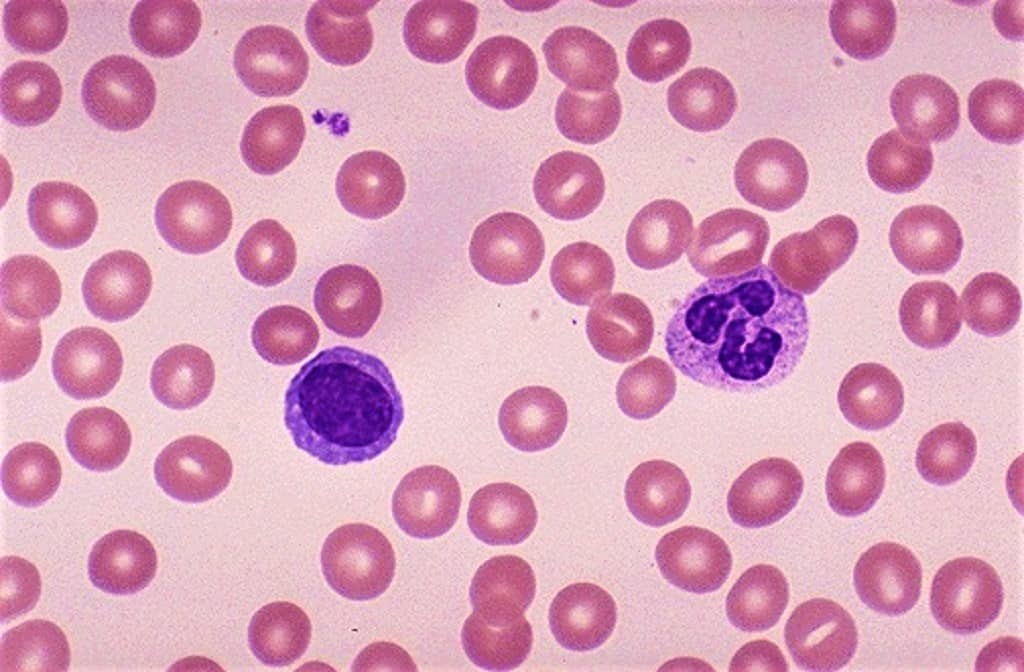
| Staining | Colors erythrocytes in pink, platelets in light pale pink, lymphocyte cytoplasm in sky blue, monocyte cytoplasm in pale blue, and leukocyte nuclear chromatin in magenta. | Colors erythrocytes in red to pink, neutrophils in dark purple nuclei, pale pink cytoplasm, reddish-lilac small granules, eosinophils in blue nuclei, pale pink cytoplasm, red to orange-red large granules, basophils purple to the dark blue nucleus, dark purple, almost black large granules, lymphocytes dark purple to deep bluish-purple nuclei, sky blue cytoplasm, platelets in violet to purple granules. |
| Significance | Staining chromosomes to identify chromosome aberrations | Staining to differentiate blood cell types. |
What Is a Giemsa Stain?
It is a stain named after the German chemist Gustav Giemsa. It helps in the diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
It comprises of a mixture of Azure B, Methylene blue, and Eosin dye. Where both azure B and methylene blue are acidic dyes while eosin is a basic dye.
Acidic dyes tend to stain cytoplasm and cell granules to pale colors while basic dyes tend to stain nucleus to dark purple or blue.
What Is Wright Stain?
It is a stain named after James Homer Wright. It helps in the differentiation of white blood cells, red blood cells, and other blood cell types.
It consists of eosin Y, azure B, and methylene blue. These dyes help to increase the brightness of the cytoplasm reddish-purple color.
Main Difference between Giemsa Stain and Wright Stain
- Giemsa stain is named after Gustav Giemsa while wright stain is named after James Homer Wrist
- Giemsa stain consists of Azure B, methylene blue, and eosin dye while the wright stain consists of eosin and methylene blue dyes.
- Giemsa stain uses both thick and thin smears whereas wright stain uses only thin smear
- Giemsa stain is used in understanding chromosome aberrations whereas wright stain to differentiate blood cell types.
Similarities between Giemsa Stain and Wright Stain
- Both stains consist of oxidized methylene blue, eosin Y, and azure B dyes.
- Both are used in differentiating blood cell types and understanding the morphology of cells
- Both are differential stains
- Both are important in cytogenetics
- Both color basic components like cytoplasm and granules
Frequently Asked Questions (Giemsa Stain vs Wright Stain)
What is Wright-Giemsa Stain Used for?
They are Romanowsky stains used to stain peripheral blood and bone marrow smears. They help to differentiate and understand the morphology of the cells.
How Giemsa Stain is Prepared?
Put 250ml of methanol, add 3.8g of Giemsa powder and dissolve. Heat the solution up to ~60oC then slowly add 250ml of glycerin to the solution. Filter the solution and leave it to stand for about 1-2 months before use.
What Does Wright Stain Test For?
It is a hematologic stain that facilitates the differentiation of blood cell types. It is classically a mixture of eosin (red) and methylene blue dyes.
Why Do Neutrophils Stain Pink?
A neutrophil is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that is characterized histologically by its ability to be stained by neutral dyes and functionally by its role in mediating immune responses against infectious microorganisms. The granules of neutrophils typically stain pink or purple-blue following treatment with a dye.
What Is Silver Staining Used For?
It is the use of silver to selectively alter the appearance of a target in microscopy of histological sections; in temperature gradient gel electrophoresis; and in polyacrylamide gels.
You May Also Like:
- Difference between Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
- Difference between Heterokaryotic and Dikaryotic
- Difference between BioCarbon and Fossil Carbon
Comparison Video
Summary
The core difference between Giemsa stain and wright stain is that Giemsa stain is primarily used in staining bacterial cells and also human cells whereas wright stain is a staining procedure of blood smears, urine samples, and bone marrow aspirates.
More Sources and References
- Giemsa stain. Wikipedia
- Wright stain. Wikipedia